osteoporosis x ray vs normal
 Radiology of Osteoporosis - ScienceDirect
Radiology of Osteoporosis - ScienceDirectMusculoskeletal Radiology / Musculoskeletal RadiologySkeletal RadiologySchool of osteoporosis Radiologist has a number of roles not only in diagnosis, but also in the treatment of osteoporosis. Radiologists diagnose fragility fractures with all imaging patterns, which include magnetic resonance (MRI) that show fractures of occult failure radiologically, but also lateral chest x-rays that show asymptomatic vertebral fractures. In particular, fragility fractures of the magnetic resonance may have a non-specific aspect and radiologists should be familiar with the typical places and findings, to differentiate these fractures of neoplastic lesions. It should be noted that radiologists do not simply need to diagnose osteoporosis-related fractures but also diagnose fractures that are complications of osteoporosis-related pharmacotherapy. In addition to using standard radiological techniques, radiologists also use dual-energy x-ray absortomy (DXA) and quantitative computed tomography (QCT) to quantitatively evaluate bone mineral density to diagnose osteoporosis or osteopenia, as well as to monitor therapy. DXA measurements of the femoral neck are also used to calculate the risk of osteoporotic fracture based on the score of the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX), which is universally available. Some of the new technologies such as high-resolution peripheral computed tomography (HR-pQCT) and MR spectroscopy allow us to evaluate bone architecture and bone marrow composition to characterize the risk of fracture. Finally, radiologists also participate in the therapy of osteoporotic fractures through the use of vertebroplasty, kyphoplasty and sacroplasty. This review article will focus on standard techniques and new concepts in the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis. RésuméLe rôle du radiologiste ne se limite pas au diagnostic de l'ostéoporose; il intervient également dans le traitement de cette maladie. Le radiologiste émet des diagnostics de fracture de fragilisation avec toutes les modalités d'imagerie, y compris par imagerie par résonance magnétique (IRM) qui révèle la présence de fractures par insuffisance invisibles par radiographie, ainsi que sur l'incidat de profil lors d'une radiographie du thorax qui Ilmount de souligner que le radiologiste ne se limite pas au diagnostic des fractures liées à l'ostéoporose. Il doit également diagnostiquer les fractures qui découlent de complications liées à la pharmacothérapie de l'ostéoporose. Outre les techniques radiologiques normalisées, le radiologue a recours à l'absorptiométrie biénergétique à Rayns (DXA) et à la tomodensitométrie quantitative (QCT) pour évaluer quantitativement l'ostéodensitométrie aux fins de diagnostic de l'ostéoporose ou de l'ostévinie La mesure par DXA du col du femur est également utilisée pour calculer le risque de fracture ostéoporotique à l'aide du système universall de cote FRAX. De nouvelles technologies, comme la tomodensitométrie quantitative périphérique haute résolution (HR-pQCT) et la spectroscopie par résonance magnétique (SRM), permettent d'évaluer l'architecture osseuse et la composition de la moelle osseuse afin de caractériser le risque de fracture. Enfin, le radiologiste é participagalement au traitement des fractures ostéoporotiques par vertébroplastie, spondyloplastie expansive et sacroplastie. Le présent article de synthèse porte sur les techniques normalisées et les nouvelles méthodes de diagnostic et de prise en charge de l'ostéoporose. Keywords Recommended articles Cite articles Metrics of the article We use cookies to help provide and improve our service and personalized content and ads. By continuing to accept . Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. or its licensors or collaborators. Direct Science ® is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V.ScienceDirect ® is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V.

in Osteoporosis | Radiology Key

Osteoporosis: Everything You Need to Know

Osteoporosis X-ray - wikidoc

Osteoporosis | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org

Osteoporosis: Don't Fall Victim to The 10 Most Common Myths

Spine fracture in osteoporosis, X-ray - Stock Image - C013/3034 - Science Photo Library
Osteopenia
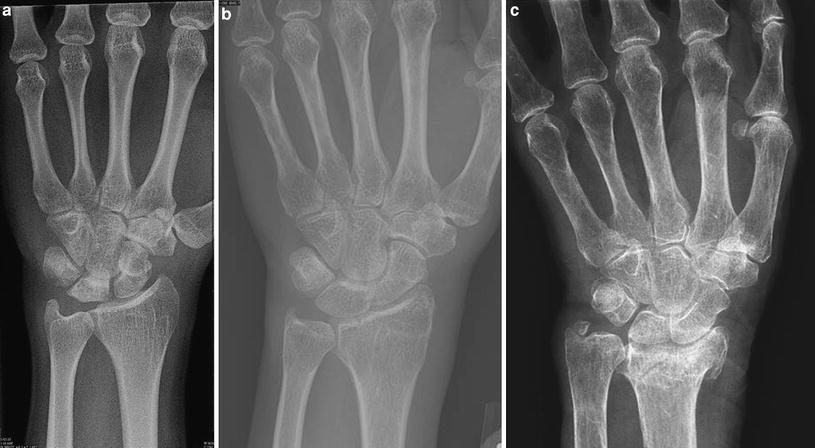
Radiography in Osteoporosis | SpringerLink

Osteoporosis Imaging: State of the Art and Advanced Imaging | Radiology
Osteopenia
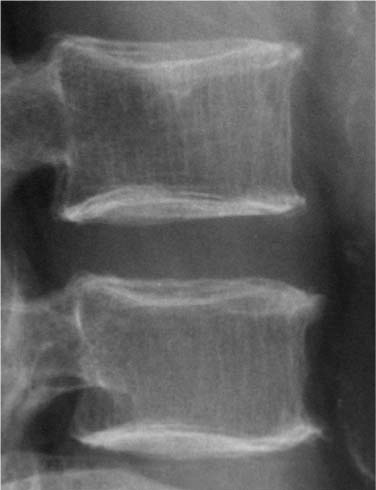
Imaging and Bone Densitometry of Osteoporosis | Musculoskeletal Key

X-ray of both knees showing osteoporosis | Download Scientific Diagram

ASPN - Simple Assessment of Global Bone Density and Osteoporosis Screening Utilizing Standard Radiographs of the Hand
Osteoporosis and Spinal Fractures - OrthoInfo - AAOS

Osteoporosis | SpringerLink
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/60649447/GettyImages_166756613.0.jpg)
Osteoporosis treatment and screening: doctors are too blasé about bone health - Vox
XSITRAY: A Database for the Detection of Osteoporosis Condition | Biomedical and Pharmacology Journal
Screening for Osteoporosis...During a Mammography? (Interview) | Medgadget

What Is Osteopenia? How Is It Different From Osteoporosis?

X-ray of Osteoporosis vs Normal Bone (Page 1) - Line.17QQ.com

Bone disease - Metabolic bone disease | Britannica

What Is Osteoporosis? Treatment, Symptoms, Medication

Radiology of Osteoporosis - ScienceDirect
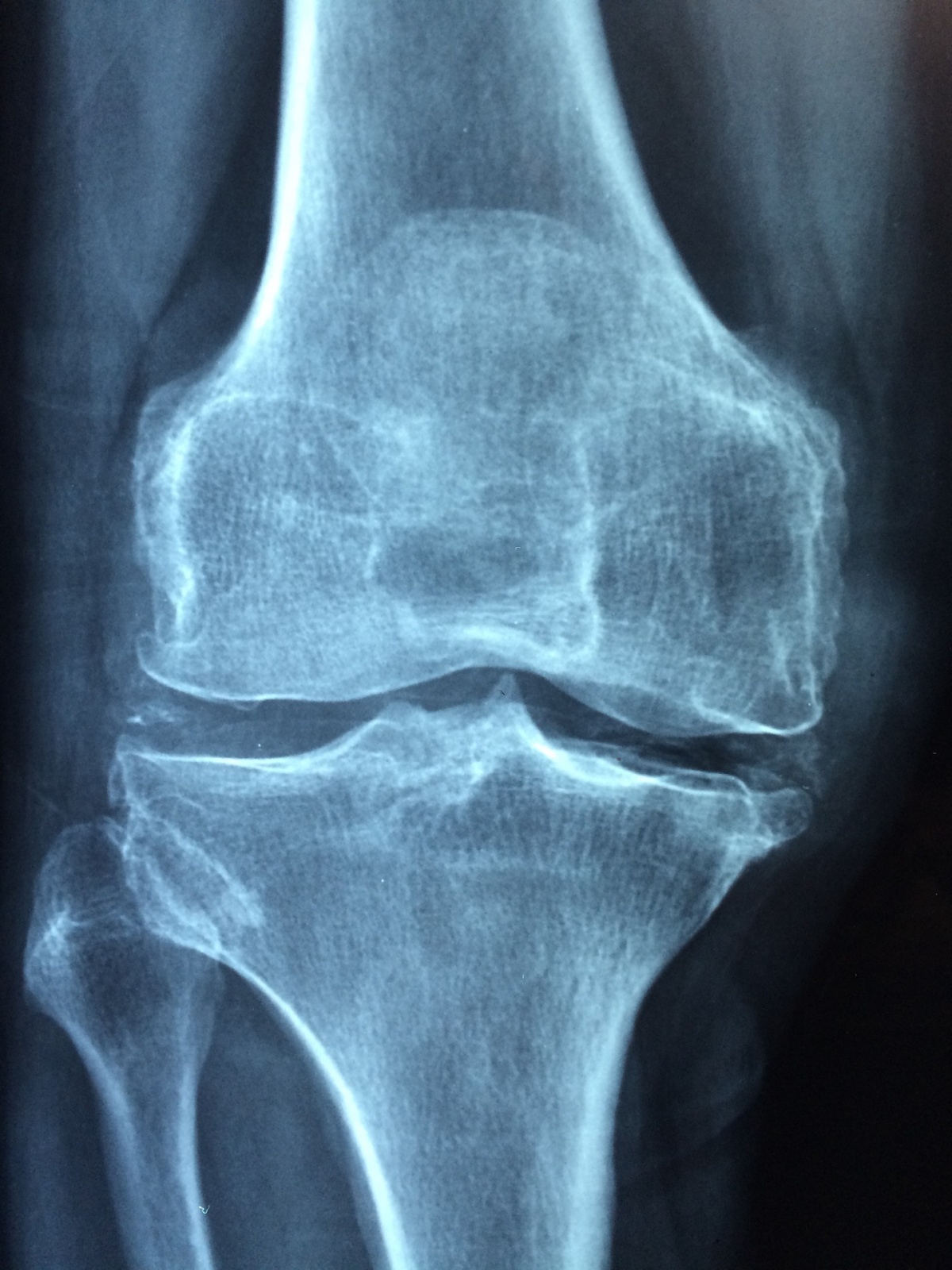
Largest ever genetic study marks likely osteoporosis treatment target

Postmenopause Osteoporosis Drug Denosumab Demonstrates Long-term Safety - Rheumatology Advisor
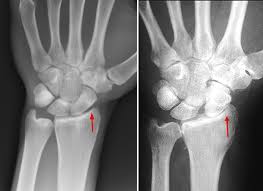
X-Rays - Physiopedia

Osteoporosis | Bone Density Loss - Diagnosis, Evaluation and Treatment
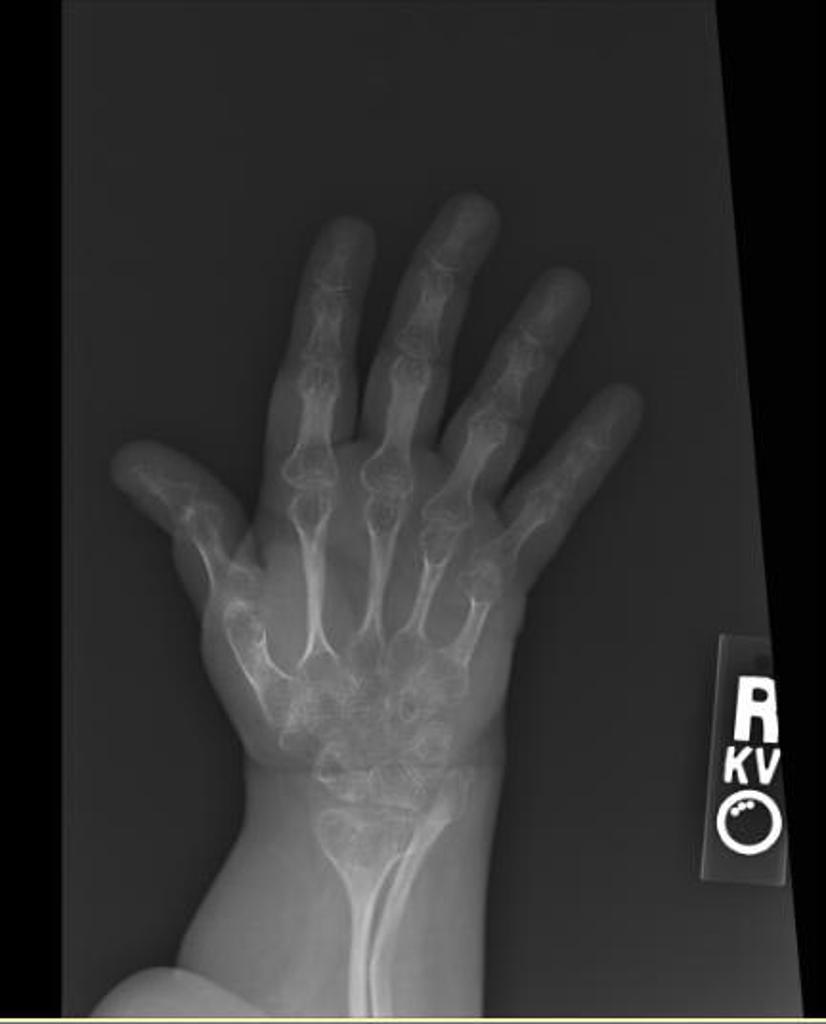
Osteoporosis X-ray - wikidoc
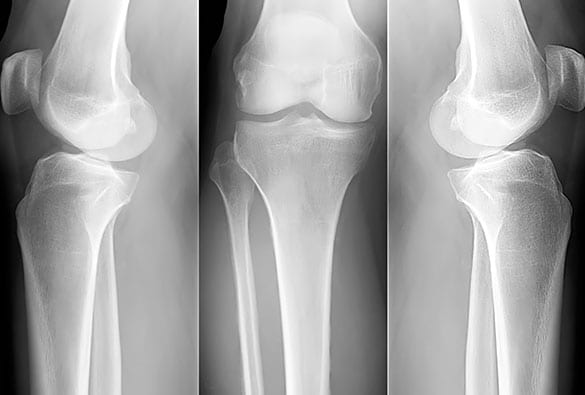
Osteoporosis | Los Angeles Orthopedic Group

Osteoporosis: What You Need to Know as You Age | Johns Hopkins Medicine

Osteoporosis X-ray (Page 1) - Line.17QQ.com
Osteoporosis: The "Thin Bone" Disease: What Women Need to Know | UC Health

Idiopathic transient osteoporosis of the hip post partum | Radiology Case | Radiopaedia.org
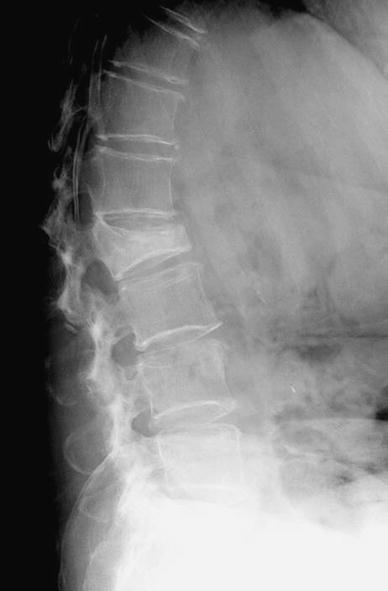
in Osteoporosis | Radiology Key

Osteoporosis - Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders - MSD Manual Professional Edition

Figure 2-5, Normal vs. Osteoporotic Bone - Bone Health and Osteoporosis - NCBI Bookshelf
Transient Osteoporosis of the Hip - OrthoInfo - AAOS

Integrated Imaging Approach to Osteoporosis: State-of-the-Art Review and Update | RadioGraphics

X-ray knee joint showing maldeveloped patella with osteoporosis in... | Download Scientific Diagram

Fractured osteoporotic hip, X-ray - Stock Image - C022/6837 - Science Photo Library
Posting Komentar untuk "osteoporosis x ray vs normal"